Performs an overrepresentation analysis, (optionally) accounting for bias.
Source:R/do.ora.R
ora.RdThis function wraps limma::kegga() to perform biased overrepresntation
analysis over gene set collection stored in a GeneSetDb (gsd) object. Its
easiest to use this function when the biases and selection criteria are
stored as columns of the input data.frame dat.
ora(
x,
gsd,
selected = "significant",
groups = NULL,
feature.bias = NULL,
universe = NULL,
restrict.universe = FALSE,
plot.bias = FALSE,
...,
as.dt = FALSE
)
plot_ora_bias(x, selected, feature.bias, ...)Arguments
- x
A data.frame with feature-level statistics. Minimally, this should have a
"feature_id"(character) column, but read on ...- gsd
The GeneSetDb
- selected
Either the name of a logical column in
datused to subset out the features to run the enrichement over, or a character vector of"feature_id"s that are selected fromdat[["feature_id"]].- groups
Encodes groups of features that we can use to test selected features individual, as well as "all" together. This can be specified by: (1) specifying a name of a column in
datto split the enriched features into subgroups. (2) A named list of features to intersect withselected. By default this isNULL, so we only run enrichment over all elements inselected. See examples for details.- feature.bias
If
NULL(default), no bias is used in enrichment analysis. Otherwise, can be the name of a column indatto extract a numeric bias vector (gene length, GC content, average expression, etc.) or a named (using featureIds) numeric vector of the same. The BiasedUrn CRAN package is required when this is not NULL.- universe
Defaults to all elements in
dat[["feature_id"]].- restrict.universe
See same parameter in
limma::kegga()- plot.bias
See
plotparameter inlimma::kegga(). You can generate this plot without runningorausing theplot_ora_bias(), like so:plot_ora_bias(dat, selected = selected, groups = groups, feature.bias = feature.bias)- ...
parameters passed to
conform()- as.dt
If
FALSE(default), the data.frame like thing that this funciton returns will be set to a data.frame. Set this toTRUEto keep this object as adata.table
Value
A data.frame of pathway enrichment. The last N colums are enrichment
statistics per pathway, grouped by the groups parameter. P.all are the
stats for all selected features, and the remaingin P.* columns are for
the features specifed by groups.
Details
In principle, this test does what goseq does, however I found that
sometimes calling goseq would throw errors within goseq::nullp() when
calling makesplines. I stumbled onto this implementation when googling
for these errors and landing here:
https://support.bioconductor.org/p/65789/#65914
The meat and potatoes of this function's code was extracted from
limma::kegga(), written by Gordon Smyth and Yifang Hu.
Note that the BiasedUrn CRAN package needs to be installed to support biased enrichment testing
Functions
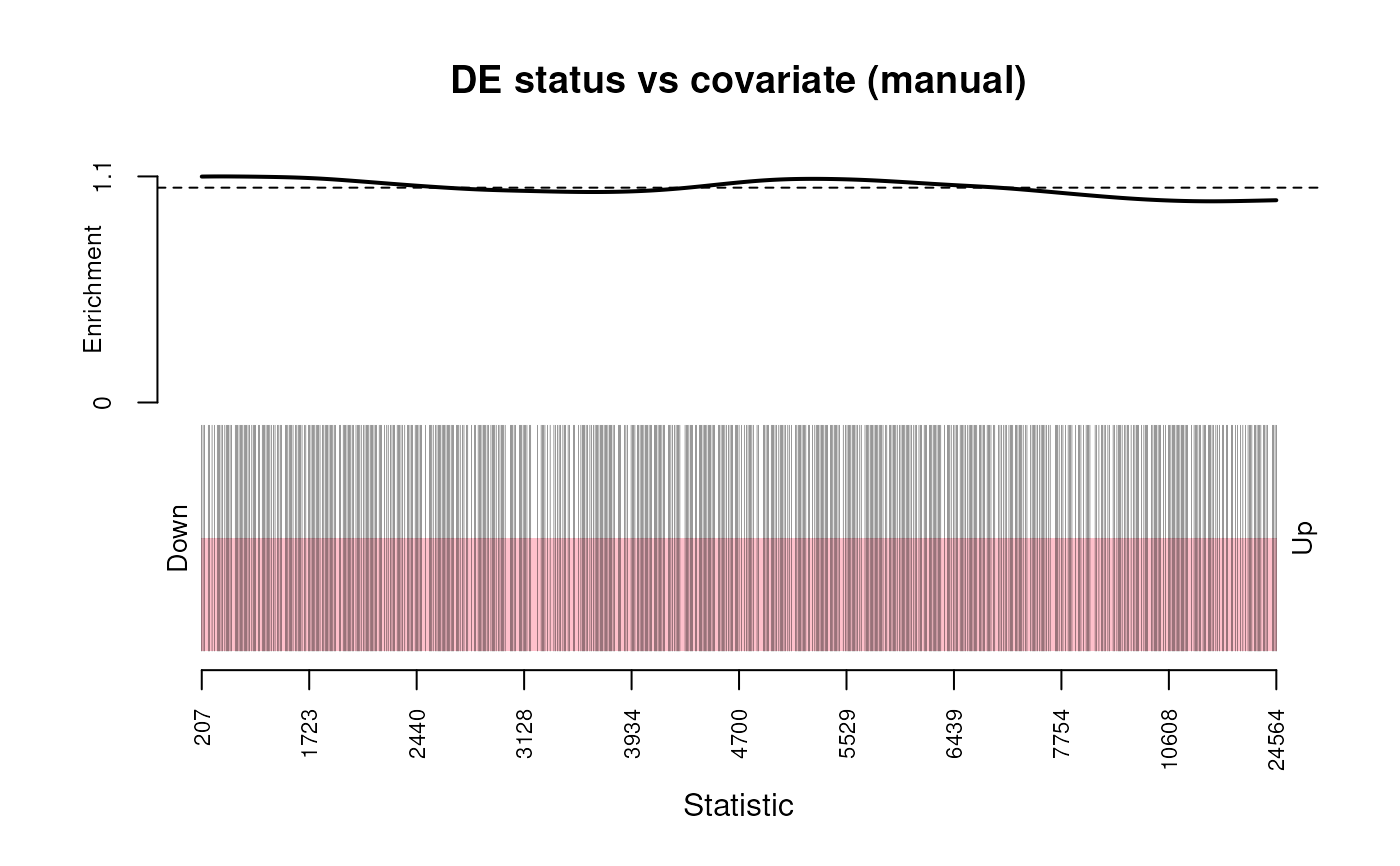
plot_ora_bias(): plots the bias of coviarate to DE / selected status. Code taken fromlimma::kegga()
References
Young, M. D., Wakefield, M. J., Smyth, G. K., Oshlack, A. (2010). Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biology 11, R14. http://genomebiology.com/2010/11/2/R14
Examples
dgestats <- exampleDgeResult()
gdb <- randomGeneSetDb(dgestats)
# Run enrichmnent without accounting for any bias
nobias <- ora(dgestats, gdb, selected = "selected", groups = "direction",
feature.bias = NULL)
# Run enrichment and account for gene length
lbias <- ora(dgestats, gdb, selected = "selected",
feature.bias = "effective_length")
# plot length bias with DGE status
plot_ora_bias(dgestats, "selected", "effective_length")
 # induce length bias and see what is the what ...............................
biased <- dgestats[order(dgestats$pval),]
biased$effective_length <- sort(biased$effective_length, decreasing = TRUE)
plot_ora_bias(biased, "selected", "effective_length")
# induce length bias and see what is the what ...............................
biased <- dgestats[order(dgestats$pval),]
biased$effective_length <- sort(biased$effective_length, decreasing = TRUE)
plot_ora_bias(biased, "selected", "effective_length")
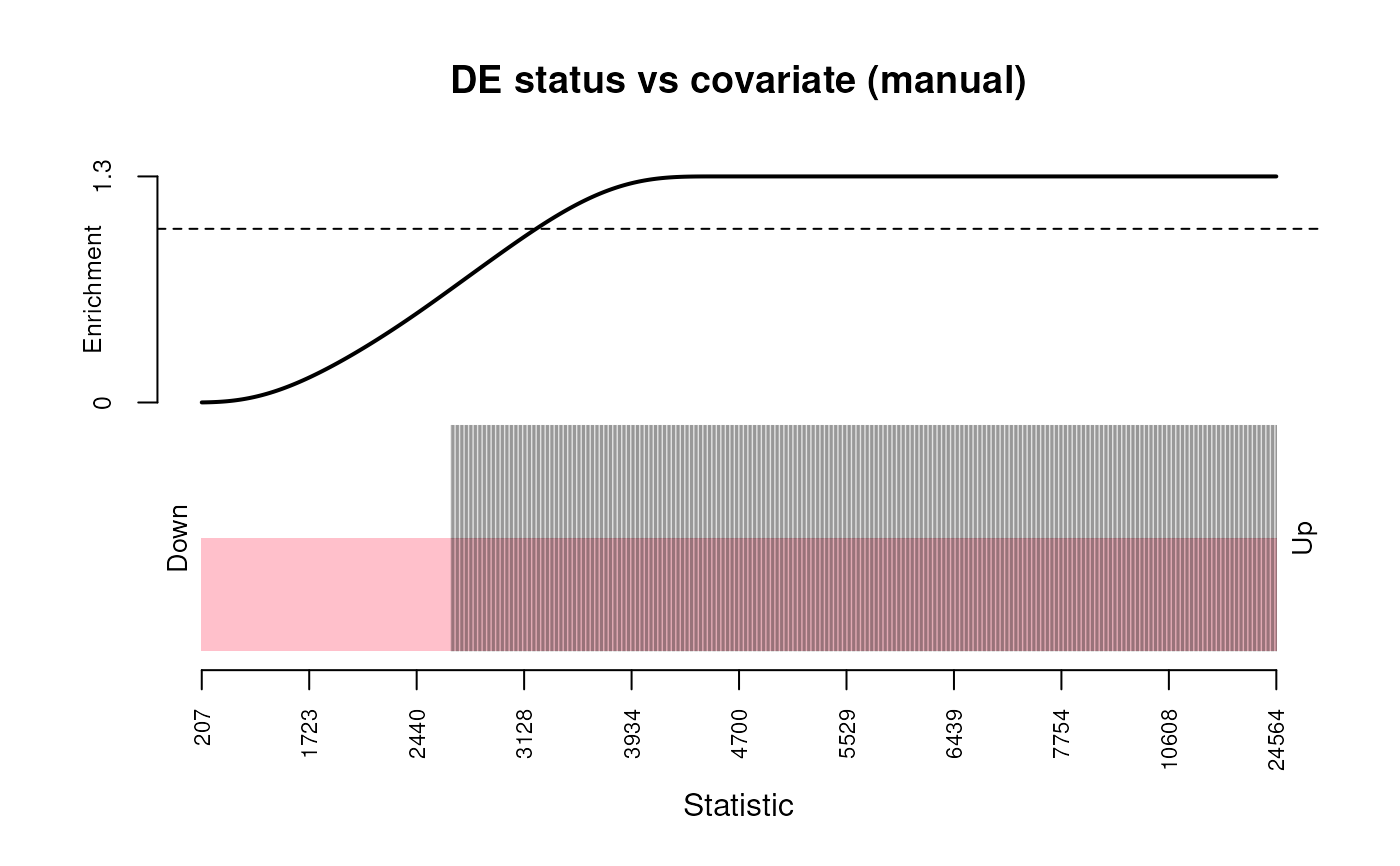 etest <- ora(biased, gdb, selected = "selected",
groups = "direction",
feature.bias = "effective_length")
etest <- ora(biased, gdb, selected = "selected",
groups = "direction",
feature.bias = "effective_length")